Laser Beam Welding (LBW): High-Precision Welding Solutions for Industrial Applications
In modern industrial manufacturing, achieving high-quality, precise metal joints is essential-especially in sectors such as pipelines, pressure vessels, and energy equipment. Laser Beam Welding (LBW) is an advanced fusion welding process that delivers exceptional accuracy, deep penetration, and minimal thermal distortion, making it a valuable solution for high-performance applications.
At FNS Pipeline Technology Co., Ltd., laser beam welding technology is applied to meet demanding requirements for precision, strength, and reliability across a wide range of industrial projects.
What Is Laser Beam Welding?
Laser Beam Welding (LBW) is a non-contact fusion welding process that uses a concentrated, coherent, monochromatic laser beam as the heat source. When the laser beam strikes the joint, its extremely high energy density rapidly melts the base material. At sufficient power levels, part of the molten metal vaporizes, forming a keyhole surrounded by liquid metal.
As the laser moves along the joint-or the workpiece moves beneath the beam-the molten metal flows around the keyhole and solidifies behind it, forming a deep, narrow weld seam with excellent metallurgical bonding.
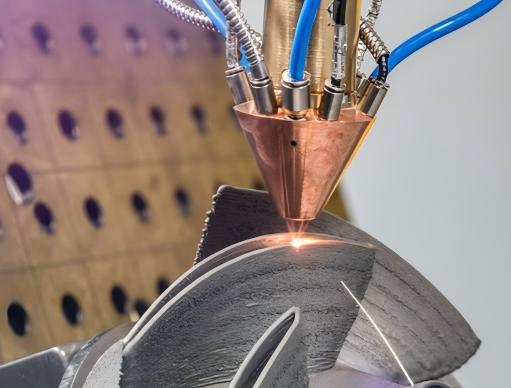
Laser beam welding process applied to industrial metal components by FNS Pipeline Technology Co., Ltd
Laser Source and Equipment Configuration
The core component of laser welding and cutting systems is the laser generator, positioned between reflective mirrors inside the equipment. Through a process known as “pumping,” atoms or molecules within the laser medium are energized beyond their normal state, producing a coherent electromagnetic radiation source—commonly referred to as a laser.
The term LASER stands for Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation. Laser beams have an extremely small cross-section and do not diverge, allowing them to be transmitted over long distances using optical fibers or reflective mirrors. With lenses or reflective focusing systems, the beam can be concentrated into a microscopic spot, achieving very high energy density.
Common Laser Types Used in LBW
Laser beam welding typically employs solid-state or gas lasers, including:
- Nd:YAG solid-state lasers, using neodymium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet crystals, with output power ranging from 1 to 10 kW
- CO₂ gas lasers, electrically excited and capable of producing continuous or pulsed beams up to 25 kW
High-power CO₂ lasers can achieve single-pass full-penetration welds in steel plates up to 32 mm (1-1/4 inch) thick, making them suitable for heavy industrial components.
Key Advantages of Laser Beam Welding
Laser beam welding offers several technical and economic benefits:
- Low total heat input, resulting in a small heat-affected zone (HAZ) and minimal grain growth
- High depth-to-width ratio, often reaching 10:1 when using keyhole welding
- Single-pass welding capability for thick materials
- Exceptional precision, ideal for thin, small, or space-restricted components
- Versatile material compatibility, including dissimilar metals with different physical properties
- Flexible beam delivery, allowing the laser source to be positioned away from the workpiece and directed around fixtures or obstacles
- No sensitivity to magnetic fields, unlike arc or electron beam welding
- No vacuum or X-ray shielding required, simplifying system integration
- Multi-station operation, where one laser source can serve multiple workstations via optical systems
At FNS Pipeline Technology, these advantages translate into higher weld quality, improved productivity, and consistent performance for pipeline and industrial fabrication projects.
Limitations and Technical Considerations
Despite its advantages, laser beam welding has certain limitations:
- Precise joint positioning is critical for consistent weld quality
- Typically requires square butt joints (I-groove) and strong clamping
- Highly reflective or thermally conductive materials, such as aluminum and copper alloys, can be more challenging to weld
- Rapid cooling rates may lead to cracking, brittleness, or porosity if parameters are not properly controlled
- High-energy laser welding can produce metal vapor plumes, which may interfere with beam penetration; this often requires plasma suppression using shielding gas
- High equipment cost, with complete systems commonly exceeding USD 100,000
Industrial Applications at FNS Pipeline Technology
Laser beam welding is widely applied in industries such as energy, petrochemical, aerospace, automotive, and pipeline manufacturing. At FNS Pipeline Technology Co., Ltd., LBW is used to support high-precision welding requirements for pipes, fittings, and structural components where strength, accuracy, and reliability are essential.
Laser beam welding represents a powerful and precise joining technology for modern industrial manufacturing. With its deep penetration, low distortion, and flexible integration, LBW provides a competitive edge for demanding applications. Backed by advanced equipment and technical expertise, FNS Pipeline Technology Co., Ltd. continues to deliver reliable laser welding solutions that meet global industrial standards.


